General information
Defectology (special or correctional pedagogy) is a science that studies the patterns of development, upbringing and education of children with physical and mental disabilities.
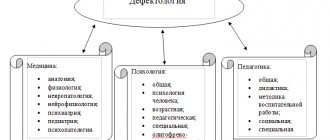
Depending on the specifics of the disorders that are subject to correction, defectology is divided into:
- Speech therapy. Specialists in this profile are involved in the correction of speech disorders in children.
- Deaf education is a field that focuses on helping children with hearing impairments.
- Typhlopedagogy. Specialists in this profile provide assistance to children with vision pathologies.
- Oligophrenopedagogy. The scope of activity of specialists in this profile includes providing assistance to children who suffer from decreased intelligence.
- Orthopedagogy. A defectologist-orthopedic teacher provides assistance to children with pathologies of the musculoskeletal system and postural disorders, as well as patients with cerebral palsy.
At the same time, the division into a narrow specialization in defectology is arbitrary, since in the process of practical activity a defectologist may encounter combined defects in which children have several different disorders at the same time (with cerebral palsy, delayed psycho-speech development, etc.). An exception is a speech therapist - this specialist teaches the correct pronunciation and writing of various units of speech to children who do not have serious concomitant pathologies.
To provide assistance to children with combined defects, a defectologist must have basic knowledge in related fields or work closely with other specialized specialists (psychologist, neurologist, neuropsychologist).
The tasks of a defectologist include:
- conducting a flexible and comprehensive study of the child’s developmental characteristics;
- assisting children in the development of attention, thinking and other basic mental processes;
- development of communication and speaking skills, formation of clear pronunciation;
- conducting intensive classes that eliminate sensory problems;
- consulting parents and training them in techniques and skills for raising a child with special needs;
- assisting the child in socialization, understanding and acceptance of himself.
To perform these tasks, the defectologist must have:
- the ability to quickly establish contact with the child and create a friendly atmosphere during classes;
- the ability to work with children according to any program that allows you to correct and compensate for developmental deficiencies;
- the ability to teach children to read and write using non-traditional methods;
- the ability to work with people of different ages according to an individual program (the defectologist also works with adults, helping to improve their social adaptation and quality of life).
Historical reference
Defectology as a science refers to the pedagogical practice of scientific knowledge of children from different age groups who have been identified with deviations in physical or mental development, as a result of which they are deprived of the opportunity to study and be brought up in normal conditions determined by the existing culture.
The term “defectology” itself comes from the merger of two words: defectus (translated from Latin - “absence” or “flaw”) and logos (translated from Greek λόγος - “teaching, word, thought”). Thus, the concept of defectology reflects the entire essence of the doctrine and is used as the title name for the branch of theoretical and practical systematic training and education of persons who have been diagnosed with deficiencies (defects) of physical or mental development.
In countries near and far abroad, this concept means a “special educational program” or “therapeutic pedagogical activity” aimed at the education of all children who are distinguished from ordinary children by the presence of developmental defects.
The history of defectology dates back to the 20th century. This industry began to actively develop from the moment the government took responsibility for mentally retarded children and adolescents. The year 1917 became decisive for this direction of scientific knowledge, when the state decided the main issue of guardianship of such children by starting the construction of several special institutions at once.
We recommend: Autism is
Outstanding personalities who made a huge contribution to the development of the science of defectology, and were also its active figures, are:
- I.V. Malyarevsky, founder of Russia’s first private children’s medical and educational institution with the goal of providing assistance to children predisposed to nervous and mental illnesses.
- L.S. Vygotsky, Russian psychologist, teacher-defectologist, experimenter, author of the book “Fundamentals of Defectology” (1934). The founder of correctional pedagogy for abnormal children, the head of a special scientific and practical institute, which is still in operation.
- ON THE. Vlasova, professor and candidate of pedagogical sciences, working in the areas of defectology and speech therapy, who was the first to use speech therapy rhythms for classes with children who stutter.
- E.K. Gracheva, Russia’s first teacher-defectologist, carried out her activities in shelters for mentally retarded teenagers and children.
- V.P. Kashchenko, the head of a unique institution that dealt with the issues of pedagogical adaptation to society of children 4-16 years old with developmental pathologies.
- G.I. Rossolimo, an outstanding psychiatrist and part-time neurologist who studied the development of children's psyche and physical health.
At the moment, many preschool institutions, schools and health-improving complexes have been opened in Russia, the main activity of which is the organization and implementation of the educational process, training, rehabilitation of children with special needs, as well as their preparation for social relationships and adaptation in the immediate environment.
What does a defectologist treat?
A speech pathologist-speech therapist does not eliminate the cause of defects, but deals with the correction of pronunciation disorders. This specialist is contacted when:
- Dyslalia is a violation of the pronunciation of sounds, which is observed in children with normal hearing and normal innervation of the articulatory apparatus. The child may not be able to pronounce the sound/sounds of one group (simple dyslalia) or several sounds from different groups (complex dyslalia). In origin, this disorder can be physiological, functional and organic.
- Dysarthria – impaired pronunciation of sounds, which provokes limited mobility of the speech apparatus (observed with lesions of the nervous system). In adults, such a disorder does not cause the collapse of the speech system, but in children it can provoke a general underdevelopment of speech.
- Stuttering is an impaired rhythm of speech, which manifests itself in frequent repetition or prolongation of speech units (sounds, syllables, words), as well as indecisiveness and frequent stops in the process of speech activity. There are neurotic and neurosis-like forms, in which motor skills are generally impaired. Speech cramps appear or worsen under stress.
- Speech disorders that are caused by hearing impairment. In children with hearing problems, all aspects of speech are underdeveloped (pronunciation of sounds, vocabulary, grammatical structure), since there is no full perception of the speech of others by ear.
- Alalia is underdevelopment or absence of speech in children who do not suffer from hearing impairment and have primarily intact intelligence. Associated with damage to the areas of the cerebral hemispheres that are responsible for speech. Damage occurs during childbirth, injury or infectious diseases.
- Aphasia – partial absence or impairment of already formed speech. Develops with tumors, hemorrhages and other organic lesions of the speech areas of the cerebral cortex. The type of speech disorders depends on the area of the lesion (sensory, dynamic, amnestic and other types of aphasia can be observed).
- Malocclusion is a dental disease that affects the correct pronunciation of certain sounds (hissing, l, r, etc.). To correct the bite and pronunciation, special plates and speech therapy exercises are used.
- Rhinolalia is a violation of sound pronunciation, which is manifested by a change in the timbre of the voice (nasality) and develops with various defects of the nasopharynx. Can be open, closed or mixed.
- Speech development delay (SDD). It manifests itself as a slower development of language norms and negatively affects the development of mental processes. May be associated with minimal brain dysfunction, hearing loss, or social factors (pedagogical neglect or overprotection).
- Psychospeech development delay (PSRD) is a complex disorder of thinking, speech, memory, behavioral skills, motor functions and emotions. With this disorder, any new skills are difficult to master, and the thought process is slow.
Children also need the help of a defectologist:
- With deafness (there is no ability to fully perceive speech). Congenital or acquired in early childhood, hearing impairment in deafness is bilateral in nature and leads to deviations in mental development.
- Hearing impaired. Hearing loss is a permanent bilateral hearing loss that causes difficulty understanding speech. Hearing impairment can be mild (difficulties arise when perceiving a whisper) or severe (the perception of spoken language at normal volume is limited). Residual hearing allows the accumulation of a limited vocabulary, but with the early development of pathology, the child does not develop speech.
- Blind or with low vision. With anomalies in the development of the visual organs, visual perception becomes impossible or severely limited (residual vision is preserved), which provokes the development of secondary deviations and causes difficulties in learning the specific meaning of words.
In addition, the defectologist deals with the correction of various disorders in:
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). With this persistent chronic syndrome, the child exhibits poor concentration, hyperactivity and lack of behavioral control (impulsivity); there may be difficulties in perceiving information and a decrease in intelligence.
- Early childhood autism (ECA). These pervasive deficits in social communication and interaction are associated with disorders of brain development. Accompanied by limited interests and a tendency to repetitive actions.
- Mental retardation (MR) is a delay or incomplete development of the psyche, which is manifested by disturbances of intelligence, speech, emotions, motor skills and will. It is congenital or acquired in nature and varies in severity (idiocy, debility, etc.).
- Cerebral palsy (CP) is a chronic non-progressive symptom complex of motor disorders that developed in connection with brain lesions in the perinatal period.
About some historical aspects
If we talk about preschool defectology as a science, then it is directly related to pedagogical practice; children of all ages are scientifically studied here. We are talking about those children who have some kind of developmental deviations, and such deviations can be of both a physical and mental nature. For such reasons, children do not have the opportunity to receive education and upbringing in the same conditions as other children, whose development is average and close to normal. That is, there is a certain culture here that some children simply do not fit into.
If we talk about the term “defectology” itself, then it comes from two words “absence” and “thought” (all this is translated from Latin). That is, it is clear what the basis is - educational and training activities for preschool children, which consist not only in theory, but also in practice, with diagnosed developmental disabilities, which can be both mental and physical.
Defectology as a branch of pedagogical science is widely developing in many countries, where we are mainly talking about a special educational program, as well as pedagogical activities of a therapeutic nature. All this is aimed at the educational activities of children who have differences in their development from others.
Defectology as a science was widely developed at the beginning of the last century, it was then that the state took on children with mental retardation at the most serious level. The time of the end of the revolution became very important for the development of such science, when the state authorities decided to seriously engage with children through the formation of specialized educational institutions, where outstanding specialists of that time worked. The preschool science of defectology has been studied at the highest level and the most serious successes have been achieved.
If we talk about the present time, then in the Russian Federation there are many organizations where preschoolers are educated. Here, all the processes by which the upbringing and training of such children are carried out are developed and organized; a very important aspect is the preparation of children for socially type relationships, and it is very important to note that such children are given the opportunity to adapt as comfortably as possible to human society.
When to contact a speech pathologist
Consultation with a defectologist is necessary if the child:
- at the age of seven months does not respond to speech addressed to him;
- does not utter “babbling” words per year;
- at 2 years old does not speak using simple words;
- at 2.5 years old is not able to construct simple sentences;
- at 3 years old, has difficulty articulating and does not swallow saliva;
- at 5 years old does not use grammatically consistent sentences in speech;
- stutters;
- does not pronounce sounds in accordance with age norms;
- is lagging behind in mental development;
- suffers from disorders of the central nervous system;
- suffers from hearing pathologies;
- has diseases of the organs of vision;
- suffers from mental disorders.
Teaching concept
The basis of defectology is the principles, the adherence to which allows for the implementation of correctional and pedagogical activities in order to promote the development and personality formation of children with disabilities within the framework of educational programs for preschoolers and schoolchildren.
For society and pedagogy, the problems of educating minors with disabilities, as well as issues of their education and socialization, are quite complex. They find their solution in pursuing the goals of defectology, namely in providing conditions for the preparation of special children, taking into account their capabilities, corresponding to age and individual criteria.
Consequently, the main goal of the science of defectology can be considered the development of problem children with their subsequent adaptation in society through special education programs, so that in the course of carrying out conscious and useful activities, organizing relationships, they do not experience complications that could cause mental disorders and destructive changes in their behavior.
Carrying out scientific activities, defectology takes into account the basic psychological and pedagogical principles that form the basis of scientific knowledge of the development of persons with disabilities:
- The principle of a single focus of the pedagogical activities carried out.
- The principle of systematization and unity of the pedagogical process.
- Humanistic approach.
- Complex techniques.
- Showing respect for the child as a full-fledged individual.
- The principle of reasonable demands on the child in accordance with his capabilities.
- Focusing on the positive aspects.
- Combining direct and parallel methods of pedagogy.
- The principle of conscious and active participation of individuals in the process of their development according to special programs (training, upbringing, education).
The principles of the educational side of defectology complement the special principles of correctional and pedagogical activities:
- The principle of uniting all diagnostic and correction processes with a single goal.
- The principle of systematic tasks that allow for correctional, developmental activities and prevention.
- The principle of studying the characteristics of a child due to his age and individuality, which are the basis of educational programs.
- The principle of unity with socially significant forces in the immediate environment.
In addition, the activities of speech pathology researchers should be aimed at developing new methods and tools that would meet the goals of science and help provide appropriate assistance to children in need, thereby supporting the principles of this area.
Consultation stages
Consultation with a defectologist includes:
- Studying the medical history and clarifying information about the course of pregnancy and childbirth.
- Conducting a comprehensive diagnosis to study mental functions (it is possible to involve a psychologist or psychotherapist in the diagnostic process). Understanding of speech, ability to engage in social contact, habits and behavior, level of intelligence, speech skills, and age-appropriateness of writing and reading are assessed. They also check concentration, memory and the emotional-volitional sphere, and the type of family upbringing is studied.
- Formation of an individual correctional lesson plan taking into account the diagnostic results. Recommendations are also given to parents regarding developmental activities at home.
Since other specialists are usually referred to see a defectologist after a diagnosis has been made, it is recommended to take the child’s medical record and the results of all available examinations at the first appointment.
If necessary, the defectologist refers the child for additional examinations - EEG, ultrasound of the brain, neurosonography, Doppler sonography, etc.
Children's speech therapist: who is he and what does he treat - MEDSI
Table of contents
- What are the responsibilities of a specialist?
- In what cases is the help of a speech therapist needed?
- Reception features
- Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
A children's speech therapist
is a specialist who identifies the causes of speech disorders in a child, and also helps him become more attentive, remember information better and, as a result, correctly construct words and sentences and pronounce them. Such a doctor has skills in the field of child psychology and pedagogy.
Children's speech therapist-defectologist
also helps improve speech skills and eliminate the causes of problems with them, but works with those types of disorders that are associated with concomitant diseases of the organs of vision, hearing and speech, the central nervous system, mental retardation, and mental disorders.
What are the responsibilities of a specialist?
A children's speech therapist has a wide range of different methods for correcting speech disorders, since in each case it is necessary to develop an individual approach. To correct speech disorders, he conducts special classes with the child, which must be regular in order to get maximum results.
The doctor helps the child master skills such as:
- Correct pronunciation of sounds (without burr, lisp, nasality)
- Competent reading and writing
- Correct composition of words and sentences
- Creating stories and retellings
- Stretching the hyoid ligament for correct pronunciation of “r” and “l”
- Speaking without stuttering
- Developing rhythm and clarity of speech
If necessary (stuttering, dysarthria, etc.), he conducts speech therapy massage. This is a method of influence in which the condition of the nerves, blood vessels, muscles and tissues of the speech apparatus changes. It is necessary to normalize the pronunciation and emotional state of the child in cases where standard speech techniques are not enough.
In what cases is the help of a speech therapist needed?
It is necessary to make an appointment with a speech therapist in cases where the child has speech disorders (pronounces sounds incorrectly, stutters), and also has a reduced understanding of the speech of another person.
Such a doctor will help with the following disorders:
- Underdeveloped speech
- Loss of speech skills
- Incorrect pronunciation of words
- Inability to construct a sentence correctly
- Problems with reading and writing
- Improper speech perception
- Inability to compose a coherent story or retell a text (for older children)
- Stuttering
- Problems with speech as a result of pathologies of the organs of hearing, vision, speech
- Impaired speech skills due to surgery or trauma to the nasopharynx
It will also help you develop the necessary rhythm of speech, learn how to breathe correctly and control your voice.
You can bring a child of any age to a children's speech therapist, but it is best to contact a specialist as early as possible (from 3 years old) so that incorrect pronunciation does not become entrenched in him.
You should contact a pediatric speech therapist-speech pathologist in the following cases:
- A 7-8 month old child does not respond to speech addressed to him
- A baby aged 1 year cannot pronounce short words (mom, dad, give, etc.)
- At the age of 2.5 years, the child does not speak or cannot formulate simple sentences from words
- Problems with swallowing, facial expressions, incorrect sense of rhythm
- The child reduces words to syllables
- Pronounces both words and sentences syllable by syllable
- Problems with concentration and memory
- Constant apathy or aggression
You can and should contact a defectologist from an earlier age, under two years of age.
Reception features
At the initial appointment, the speech therapist finds out the child’s vocabulary, the correctness of his sentence construction, pronunciation and his communication skills. For older patients, the ability to write and read, as well as creative thinking, are important.
If you contact a defectologist, additional types of examinations may be required: Dopplerography of the brain, electroencephalography, spondylography, etc. (depending on concomitant symptoms).
The development of a training program takes place according to individual parameters, since in each situation not only the types of speech problems differ, but also the reasons for their occurrence.
Training takes place in a playful way to make it easier for children to remember information and develop the necessary skills. This format helps the child and does not frighten him, and also keeps him interested for the time necessary for training and correction.
A children's speech therapist and defectologist develop recommendations according to which parents should work with their child at home in order to consolidate the results of treatment as quickly and effectively as possible. These can be special exercises and educational games.
Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
- The MEDSI network of clinics has extensive capabilities for comprehensive diagnostics and clarification of the causes of speech disorders: the latest expert-class equipment
- Reception is conducted by experienced, highly qualified doctors of various profiles: neurologists, psychologists, teachers, speech therapists, defectologists, neuropsychologists, who regularly take advanced training courses in leading clinics in Russia and abroad
- You can make an appointment for a consultation with a children's speech therapist at a time convenient for you by calling 8 (495) 7-800-500
- Clinics are located in all districts of Moscow within walking distance from the metro station
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is carried out taking into account examinations of the organs of vision and hearing - if there are problems with speech or hearing pathologies, tasks of a visual nature are offered (speech instructions are kept to a minimum), and if vision is impaired, they are offered orally.
For diagnosis the following are used:
- a method of conversation, during which the features of the child’s ideas about himself and the phenomena of the surrounding world, habits, fears and level of adaptation are clarified (questions are asked in a form understandable to the child);
- an observation method in which a defectologist observes the child’s play activities;
- projective techniques;
- tests (most often the D. Wechsler test adapted for children is used);
- experimental psychological methods.
When conducting examinations, the defectologist pays attention to the child’s emotional reaction to the examination, the adequacy of the perception of instructions and goals of the tasks, the nature of the activity when performing and the reaction to help in solving the task, the emotional reaction to the result of completing the task, etc.
What is the teaching concept?
Modern preschool defectology is based on principles through which it is possible to act using both correctional and pedagogical methods. Such scientific activity has the main goal of maximizing the development of children with certain pathologies and doing everything to develop them as individuals. All this is reflected in educational programs for preschool children.
If we talk about social society and pedagogical activity, then raising preschool children who have certain defects (here we can talk about physical and mental disabilities), then this seems to be a rather difficult task. The same can be said about the way they learn and socialize. However, there are solutions for the purposes of defectology, that is, everything must be done to provide conditions for children with certain anomalies to prepare for the educational process, while their capabilities, age and individual criteria must be taken into account. Everything is done to ensure that education helps such children adapt to real life as much as possible.
Based on all of the above, we can say with confidence that the main goal of such a science as defectology is the developmental process of children with certain problems who require subsequent adaptation in modern society so that they are given the most complete education. For this purpose, special educational programs are actively used; such education contributes to the implementation of useful and cognitive activities, so that such children do not experience any complications in organizing relationships. Since it is often they who become the cause of various kinds of deviations and changes of a destructive nature in the behavior of such children.
There is also retraining of defectology educators for whom defectology is a vocation, so that their activities are carried out in the most effective manner.
Principles of work in Kursk
After the diagnosis, the speech therapist develops an individual lesson plan for each child. In more severe cases, close cooperation with a neurologist, otolaryngologist, psychologist and treating pediatrician is possible.
The range of specialist tasks is not limited to sound production. Most often, the work consists of several stages:
- Development of memory, attention, perception and thinking of a child.
- Establishing correct breathing.
- Development of fine and gross motor skills.
In addition, the teacher pays sufficient attention to intonation, grammatical and phonetic components. Classes help increase your child's vocabulary and develop coherent speech. In the process of interacting with young patients, specialists use exciting gaming techniques to better perceive information and reduce workload.
The materials are reinforced with homework, which the student completes jointly with his parents. This tandem ensures positive dynamics and obvious progress.
Every parent should remember that a referral to a speech pathologist is not a death sentence, but an opportunity to promptly eliminate speech defects in a child and achieve his successful social and educational adaptation.