What are soft sounds?
To find out what soft sounds are, let’s compare two words and pay attention to the pronunciation of their initial sounds: “side” and “run”
The first word contains a voiced consonant [b], in the formation of which the lips participate: side [b o k]
The initial consonant sounds quite hard. Compare with the pronunciation of the second word: run [b' e k]
The first voiced consonant is indicated by the same letter “b”, but it sounds slightly different. When pronouncing it, the back of the tongue rushes towards the hard palate, arching like a bridge. Narrow passages for exhaled air are formed on the sides of the tongue, as a result of which the voiced consonant acquires softness, or palatality. The linguistic term "palatality" comes from the Latin word palatum, which literally means "palate".
So, in Russian speech, hard and soft consonants are distinguished.
Compared to hard consonants, all soft sounds during formation are distinguished by the additional participation of the tongue. Soft consonants are noisy sounds, in the formation of which there is additional articulation of the tongue to the palate.
Softness
Only consonant sounds can be soft; the term “soft consonant letters” does not exist in the Russian language, since a letter is just a symbol of the alphabet.
Consonant sounds are called soft because when pronouncing such consonants, the middle back of the tongue is raised towards the hard palate to cause the so-called softness.
To understand how to determine the softness of a consonant sound, you need to monitor the movement of the tongue when pronouncing a particular word.
Softness as an element of transcription has its own designation: '.
In writing, gentleness is expressed in two ways:
- using the vowels i, e, ё, i, yu, which indicate the softness of the previous consonant sounds;
- using a soft sign (b).
A consonant sound is soft not because softness indicators are placed after it; on the contrary, softness indicators are placed after a consonant sound if this consonant sound is soft.
The concept of voiced and voiceless sounds
In Russian speech, in addition to hardness and softness, a distinction is made between sonorous and dull sounds. Phonetics gives a clear idea of whether a consonant sound will be voiced or unvoiced.
Voiced sounds are produced by speech when air noisily overcomes an obstacle in the mouth and vibration of the ligaments occurs.
| Voiced sounds | Muffled sounds | ||
| [b] | [and] | [To] | [X] |
| [V] | [h] | [P] | [ts] |
| [G] | [l] | [With] | [h] |
| [d] | [m] | [T] | [w] |
| [th] | [n] | [f] | [sch] |
Voiceless consonant sounds are spoken exclusively with the help of noise; the voice is not involved here, and the vocal cords are in a relaxed state.
In many schools, teachers teach children the following phrase: Styopka want some cheek? Fi!. Here are consonant sounds that are unvoiced in Russian.
To remember and distinguish voiced consonants from deaf ones, we divide them into pairs. There are 11 of them in total, if you take into account soft consonants (with the exception of [zh]-[sh]) [b]-[p]; [v]-[f]; [g]-[k]; [d]-[t]; [h]-[s].
So, we found out that letters in the alphabet make several sounds. It depends on the position of the letter in the word. At the end of a syllable, the voiced sound is muffled, the same happens if the letter comes before a voiceless consonant, for example golu b ka. In writing we use a voiced consonant, but we say golu p ka.
Distinctive features of soft and hard sounds
What sound comes after a consonant:
- If after a consonant there is a vowel a, o, u, e, s, then the consonant is hard.
- If after a consonant there is a vowel and, e, yu, i, then the consonant is soft.
Practice with examples: In the words “mother” and “nora” the consonants are hard, because they are followed by “a” and “o”. In the words “fly” and “nanny” the consonants are soft because they are followed by “e”, “i”, “ya”.
- If another consonant sounds after a consonant, then the first consonant will be hard.
- There are sounds that can only be hard and sounds that can only be soft, no matter what sound is heard or what letter is written after them.
Always hard sounds - zh, sh, ts. Always soft - th, h, shch. A common way to learn these sounds is a simple technique: we write the letters that convey these sounds on a line, and emphasize “th, ch, sch.” The underscore symbolizes the cushion on which the soft sounds sit. The pad is soft, which means the sounds are soft.
Soft sign and hard sign
- If there is a consonant at the end of a word and the letter “b” after it, then the consonant is soft.
This rule is easy to apply if the child sees the written word, but it will not help if the child performs the task by ear.
Movement of the tongue when pronouncing soft and hard sounds
When pronouncing a soft sound, the tongue moves slightly forward, approaching (or touching) the palate with its middle. When pronouncing hard sounds, the tongue does not move forward.
How to explain hard and soft consonants to a child
The task is not easy. If your child knows letters, start with a simple story about how vowels surrounded consonants and began to command them. Yes Yes. In war it’s like in war. These sassy vowels decide whether the consonant sound will be hard or soft.
There are a couple of rebels to whom this rule does not apply.
C, Zh, Sh are only hard, and Ch, Shch and Y are soft under any circumstances. We blacklist rebels and place it on the most popular place in the house, for example, on the refrigerator, so that their glorious names are imprinted in the child’s memory. Don’t forget about the soft sign, which, by its appearance, easily decides the fate of hard and soft consonants.
The rest were less fortunate: if after a consonant there is an A, O, U, E or Y the sound is hard, it is indicated by a blue brick or circle, if the prisoner is followed by an E, E, Ya, Yu or I it is soft and is indicated by green.
Did your efforts not bring the expected results? Draw attention to the position of the tongue when pronouncing paired hard and soft consonants.
Offer to turn a hard sound into a soft one, using different vowels: pa pya, sa sya, pu pyu, su syu, etc. A similar game can be complicated by changing the words: angle coal, rad row, bow hatch and others.
If after a consonant there is its equally consonant brother, the sound is hard. For example, in the word candy after n there is f. We can confidently say that in this case n is solid.
By developing the ability to distinguish between hard and soft consonants, you help the child develop auditory attention and phonemic awareness, which is important when teaching a child to read and write. This way you lay the foundation for success in school.
Remember that Russian is one of the most difficult languages. It is not so easy to explain hard and soft consonants to a child. Therefore, you should not reproach your baby for mistakes.
Dear readers! We are sure that now you know how to teach your child to distinguish between vowels and consonants, hard and soft sounds and letters. Share your successes and secret techniques in the comments.
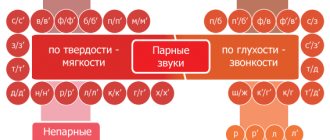
Paired hard and soft consonants
Many voiced and voiceless consonants in the Russian language are distinguished by the sign of hardness/softness and form correlative pairs:
With the help of hard and soft consonants you can distinguish between words:
- rad - row;
- howl - howl;
- son - blue;
- magician - moment.
Several consonant sounds do not have a hard/soft pair. Always hard consonants are the sounds [zh], [sh], [ts]. In any position in a word they sound only firmly:
- fat [f y r]
- silk [s h o l k a v y ']
- citrus [ts y tr rus].
Letters that represent only soft consonants
The letters th, ch, shch always denote soft consonant sounds: [th'], [ch'], [sh'].
The following rule applies here: these soft consonants always remain soft, regardless of the subsequent vowel letter.
Letters that represent soft and hard consonants
The letters b, c, d, d, z, k, l, m, n, p, r, s, t, f, x can denote both hard and soft consonant sounds. This is reflected in the following table:
| Letters | Sounds |
| b | [b], [b'] |
| V | [in], [in'] |
| G | [g], [g'] |
| d | [d], [d'] |
| h | [z], [z'] |
| To | [k], [k'] |
| l | [l], [l'] |
| m | [mm'] |
| n | [n], [n'] |
| P | [p], [p'] |
| R | [р], [р'] |
| With | [s], [s'] |
| T | [t], [t'] |
| f | [f], [f'] |
| X | [x], [x'] |
The consonants presented above are called paired according to softness and hardness.
When comparing the words mom ([mama]) and mint ([m'ata]), one can come to the conclusion that in writing both words use the same letter - m, but the pronunciation of the sounds is different. Only in the second case is the consonant sound soft. This example shows the relationship between a consonant letter and the vowel letter behind it.
Division into vowels and consonants
First of all, the child must learn that all letters, except for the soft and hard signs, represent certain sounds. While learning the alphabet, you need to help your child remember that sounds are divided into vowels and consonants. It is important to explain to the first grader that neither b nor b have anything to do with vowels or consonants. They are only helpers, making a consonant soft or hard.
How are hard and soft sounds indicated in writing?
In writing, the hardness and softness of consonant sounds are indicated only when writing a transcription. To indicate a soft sound, use the apostrophe "`". Hard sounds are not distinguished by any signs in writing.
Below is an explanatory table that clearly shows that the same sound can be both hard and soft, depending on which vowel follows it.
Table with examples of writing sounds in soft and hard use
| ram | [b] | [b`] | underwear |
| pile | [V] | [in`] | elm |
| hump | [G] | [g`] | weight |
| house | [d] | [d`] | uncle |
| gold | [h] | [z`] | Earth |
| cat | [To] | [k`] | whale |
| skis | [l] | [l`] | lemon |
| garbage | [m] | [m`] | ball |
| Nora | [n] | [n`] | Nyura |
| floors | [P] | [n`] | singing |
| robot | [R] | [r`] | river |
| Sun | [With] | [s`] | seed |
| tone | [T] | [t`] | crown |
| furore | [f] | [f`] | the final |
| hamster | [X] | [x`] | hut |
You can notice that consonant sounds form pairs based on hardness-softness: [v] - [v`]; [k] - [k`], etc. In writing, both hard and soft sounds are indicated by the same letter, but are pronounced differently. With the help of such a table, children can more easily understand the hardness and softness of consonant sounds, while remembering that the sign “b” always makes the consonant soft, and the sign “b” always makes the consonant it follows hard.
Additional signs by which a consonant sound can be classified into one category or another
A certain combination of organs of the articulatory apparatus is responsible for the pronunciation of each sound. Children can be taught how to easily recognize soft and hard consonants by the position of their lips.
If, while pronouncing syllables, a child smiles, that is, the corners of his lips move to the sides, then such syllables contain soft consonant sounds. If you don’t want to have fun when pronouncing a syllable, then a hard consonant comes across the baby’s path. This will make learning soft and hard sounds easier and more fun.
How to teach a child to distinguish between hard and soft sounds
Examples of interesting tasks for developing the skill of distinguishing between soft and hard consonants
A picture or simply a list of thematic words is shown, and the task is given to choose words with soft or hard consonants. For example:
Examples of tasks for children
Tasks for training the differences between paired consonants can be compiled for each pair according to the following principle (using the example of the D/T pair):
Tasks for distinguishing a pair of consonants G/K
Guess
We write signs with transcriptions of words. The child’s task is to name the word and name soft sounds. It is best to make the signs bright and large, then it will be more interesting for children to react to them.
To start the game, select easy words: [m`el]; [soap]; [l`uk]; [WHO]. And at the end you can complicate the task and give the following words: [b`elka]; [ski track]; [kl`on].
While playing, the child visually remembers the designation of soft consonant sounds and gains practical skills in using knowledge when writing.
How to introduce a first grader to hard and soft consonant sounds in a playful way?
- After writing down pairs of words that include soft and hard consonants, you can ask your child to highlight certain sounds with the following colors:
- vowels in red;
- hard consonants in blue;
- soft sounds in green.
- Parents can name words for their children by asking them to identify the hard and soft consonant sounds in them by ear. For the first attempts, you should select three-letter words starting with a consonant. As the child’s skills in identifying soft and hard sounds improve, the length of words needs to be increased, and the task must also be made more complex, starting words with a vowel and including hard or soft signs in them.
- You can modify the previous game by changing roles. Let the student come up with words ordered by the parent. For example, the elder will ask you to name a word of five letters, while the first must be a vowel, and the presence of a soft consonant B is required. The answer may be an RESULT or a WRAP. By showing imagination, you can make the task even more difficult. For example, name words by category (food, sports, travel, summer, etc.).
- You can also play using various kinds of objects. Balls, colored cubes, jump ropes, and cards with numbers are great for learning the classification of consonant sounds. The latter can be used in the case when a first-grader needs to determine which sound in a word is soft or, conversely, hard, or how many different sounds there are in a given word. You can throw the ball, calling the required sound, and jump on the rope if you make a mistake.
- An interesting educational game can be played with cubes of four colors: red, blue, green, yellow. Each cube is needed in a quantity of several pieces, because it is easy to guess what sounds they will represent. The yellow color is additional, the one that was not described earlier, will mean a hard or soft sign.
There are many variations of this game, below are just the main ones:
- The driver lays out a diagram of the word from the cubes, and the player selects the appropriate word from it. Thus, the scheme: GREEN RED BLUE GREEN RED GREEN YELLOW corresponds to the word BEAR. You can make the task more difficult or easier by reducing or increasing the number of cubes or colors. The main factor is that the first grader takes not only the place of the player, but also the driver, that is, he performs the task of both selecting a word and drawing it up schematically.
- You can add a rating to the game, using the sum of points scored to determine the winner at the end of the competition. Determining in turn the roles of the driver and the guesser, guess the word, and give a certain number of points for each color of the cube. For guessing the letter indicated by the yellow cube, count five points, because in its place there can only be two letters; for the sound hidden under the green and blue colors, fifteen each; and for the vowel indicated by the red cube - ten. Soft and hard consonants add up to 36 sounds, so finding them is more difficult than lower vowels.
- As in the previous game, you can add a distinction by category here. However, here it will be more of a hint than a complication. After narrowing the search range, the word will be found easier and faster.
- For children just starting their journey in the phonetics of the Russian language, you should select a game program that is somewhat simpler than the previous ones. For example, you can list various objects located in the apartment in order to use such a clear example to explain which sounds in a word are soft and which are hard. In such an activity, preference is given not only to the clarity of the subject, but also to speaking out loud. If there is a board in the room, it is best to write the word on it, dividing it into syllables and determining the gradation of sounds with the child. You can also use a regular sheet of paper for writing, then with the help of colored pencils it will be possible to use the color designation that is offered in the previous game.
- The next game is best played in a group of several children. Depending on the skills of the other students, the first player names a word of any length and complexity, the next participant spells out this word, naming the degree of each consonant sound (whether it is soft or hard). Having indicated everything correctly, the player comes up with a word of the same difficulty for the next one, and so on in a circle. The person who answers incorrectly leaves the game, and the last remaining participant becomes the winner.
- As soon as it becomes clear that your elementary school student has become familiar with the basics of parsing consonant sounds, you can move on to the most serious task: composing a fairy tale from words chosen by dad or mom. Having made a diagram of colors and putting these schemes into sentences, the adult, with hints, helps the child come up with a short story similar to the word BEAR compiled above. The scheme should be prepared and thought out in advance, which adds certain difficulties and time costs, however, as practice shows, first-graders love this game the most.
Use these games and exercises not only during studying at home, but also while walking, traveling on the bus, etc. And soon your child will distinguish between hard and soft consonant sounds in 1st grade no worse than his classmates.