Article:
Mental retardation is one of the most common childhood pathologies. About 50% of all low-achieving schoolchildren are diagnosed with this condition. Moreover, most of them study in regular general education schools, not correctional schools, despite the fact that they are not able to master the knowledge provided for in traditional programs. As a result, a lot of problems arise for teachers (how to teach) and parents (how to develop). In fact, mental retardation in children is not a death sentence at all. Competent and regular classes are a guarantee of successful psychocorrection work.
What it is
Mental retardation is a mental retardation when the basic cognitive functions (thinking, memory, attention, emotional-volitional sphere) in a child are not as well developed as those of peers and differ from the norms established for a given age. Diagnosed only in children of preschool age or primary school. If signs of the disease remain at the time of transition to secondary care, more serious diagnoses are made - for example, constitutional infantilism or mental retardation.
The term was proposed by the Soviet psychiatrist G. E. Sukhareva in 1959. Widely used in psychological, pedagogical and medical practice and literature. However, at the end of the 90s of the 20th century it was considered too generalized and already outdated, so the question of its replacement was raised. In 1997, this diagnosis was withdrawn from use by order of the Ministry of Health. They have been replaced by new concepts corresponding to codes F80–F89 and F90–F98 in ICD-10. These include all kinds of psychological development disorders (but no longer mental disorders):
- expressive and receptive speech disorders;
- hyperkinetic disorders;
- dyslexia;
- dyscalculia;
- dyspraxia;
- dysgraphia;
- behavioral disorders;
- phobias;
- tics;
- enuresis;
- encopresis;
- stuttering.
Since 1997, the term is not applicable as a medical diagnosis and is not opposed to mental disorders. However, this concept continues to be widely used in Russian-language psychological and pedagogical literature and Russian educational institutions.
Causes
All causes of mental retardation are divided into two large groups.
Biological
Pathologies and complications during pregnancy:
- if the mother suffered severe toxicosis, infection, intoxication, or injury during pregnancy;
- multiple births;
- intrauterine fetal hypoxia;
- prematurity;
- asphyxia;
- Rhesus conflict;
- incorrect presentation;
- birth injuries.
Infectious, toxic and traumatic diseases leading to perinatal encephalopathy in the first years of a baby’s life:
- nuclear jaundice;
- operations under anesthesia;
- fetal alcohol syndrome;
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- minimal brain dysfunction, organic brain damage, traumatic brain injury;
- congenital visual and hearing impairments;
- low mobility;
- asthenia;
- malnutrition, neuroinfections, influenza, rickets, hydrocephalus, vegetative-vascular dystonia, epilepsy.
Biological reasons also include genetics. There are cases when deviations of this kind are diagnosed from generation to generation.
Social
These include:
- long-term limitation of life activity;
- social deprivation;
- communication deficit;
- unfavorable upbringing conditions;
- mild mental disabilities in parents;
- psychotrauma.
Among the unfavorable conditions of upbringing that lead to mental retardation, there are three most common ones.
Neglect
A child to whom parents do not pay sufficient attention from early childhood, do not engage with him, do not develop him, grows up to be affectively labile, impulsive and suggestible. Does not learn basic rules of behavior and has no intellectual interests. Successful learning requires a basic understanding of the world around us. Reminds me of Mowgli who found himself in civilization. As a result, abnormal personality development is diagnosed as mental instability. But this is not the same as pedagogical neglect.
Overprotection
A child who, from early childhood, is given too much attention by anxious and suspicious parents and is raised as a little “god” of the family. He does not know how to overcome difficulties on his own, or adequately correlate desires and needs with the necessary efforts. There is no willpower. This leads to emotional lability, lack of initiative, self-centeredness, and dependence on adults. As a result, psychogenic infantilism is diagnosed.
Authoritarianism
A child who is suppressed by authoritarian parents from early childhood experiences their aggression, rudeness, cruelty, and despotism. Physical violence is often used. Against such an unfavorable background, obsessions, indecision, phobias, neuroses, increased levels of anxiety, and autism develop. This is an emotionally immature person who is not aimed at achieving success. As a result, learned helplessness syndrome is diagnosed.
Clinical picture
Parents should be aware of the main symptoms of mental retardation characteristic of a particular age.
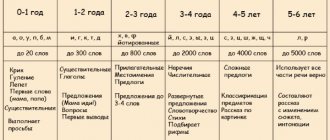
1 year
CPR is not diagnosed at 1 year of age. But a number of alarm bells may indicate a tendency towards it:
- Compared to his peers, the baby began to hold his head up, sit up, crawl, turn, stand up, walk, walk late;
- does not hold objects well;
- cannot coordinate movements;
- moves little;
- unemotional.
In this case, it is necessary to take into account the individual developmental characteristics of the baby and, if in doubt, consult a pediatrician or neurologist.
2 years
Deviations are indicated by:
- ignorance of one's own name;
- lack of response to the simplest questions;
- profuse drooling;
- sleep disorders;
- moodiness, tearfulness, irritability, aggression;
- difficulty maintaining attention on a specific subject.
3 years
- Poor vocabulary (no more than 20 words);
- speech defects;
- lack of basic understanding of the surrounding world (cannot name animals, household items, body parts);
- inability to formulate coherent speech;
- difficulty completing basic tasks;
- undeveloped imagination;
- uniformity of actions in the game;
- inability to concentrate;
- fast fatiguability;
- aggressiveness, hysteria.
4 years
At 4 years of age, mental retardation is already clearly diagnosed based on specific symptoms.
Physical:
- weak muscle tone;
- kinetosis;
- urinary disorders;
- headache;
- fatigue, weakness, lethargy, immobility.
Cognitive:
- inability to speak coherently;
- poor vocabulary;
- absent-minded attention;
- poor memory;
- inability to remember information visually or auditorily;
- lack of basic knowledge about the world;
- lack of formation of cognitive motivation.
Social:
- aggressiveness, distrust, wariness towards others;
- isolation, autism, self-absorption;
- reluctance to participate in joint games;
- infantilism;
- mood changes.
It is at the age of 4, with timely recognition of mental retardation, that corrective work must begin. In its absence, all these symptoms only increase and deepen at 5-6 years of age. Secondary signs appear: psychosomatic diseases and internal complexes develop, cognitive abilities deteriorate, and social maladaptation is observed.
At primary school age, mental retardation manifests itself more clearly. Such children differ from their peers in behavior and learning abilities. If parents and kindergarten teachers missed this moment and sent such a child to school, the teacher can no longer help but pay attention to this. He needs to master the minimum standard program, without which he cannot transfer such a student to another class. Therefore, at this stage, a medical-pedagogical commission is organized, a diagnosis is made and psycho-correctional work begins.
How to treat children with RRD, ZPR, ZPRR, VMTMR in Saratov, in Russia
Since the beginning of work at Sarklinik, 4,726 children with mental retardation, mental retardation, mental retardation, and vegetative retardation have undergone comprehensive treatment. Sarklinik knows how to treat delayed speech development in a child, how to treat delayed psycho-speech development in children , ZRR, ZPR, ZPRR, ZPMR, how to cure ZPR, ZPR, ZPRR, ZPMR, ZNPRR, how to get rid of developmental delay in boys and girls. Treatment methods have proven themselves over many years. Mild, moderate, and severe delays in psycho-speech development are treated. Sarclinic works with serious diagnoses, when parents have less and less hope for recovery. Unfortunately, in such cases, as a rule, multiple courses of complex treatment are required, as a result of which memory, thinking, speech, and motor areas are improved. Recommendations are also given to parents on further rehabilitation of children. Children are treated: 3 months, 4 months, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 months, aged 1 year, 2 years, 3 years, 4 years, 5 – 16 years. On the medical website sarclinic.ru you can read patient reviews for free online to the doctor.
Comprehensive rehabilitation! Is your child developmentally delayed? Contact Sarklinik!
Sign up for a consultation. There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Photo: (©) Mb2006 | Dreamstime.com \ Dreamstock.ru The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Why does a child feel bad, doesn’t speak much, doesn’t speak, how to teach a child to speak, talk
Which doctor treats enuresis in children? Who to contact if you have enuresis in Russia?
Children's nocturnal enuresis: treatment, causes, how to treat in Russia, Saratov
Why does a child stand on tiptoes, toes, poorly on his legs, not worth it: what to do, how to treat, stand
Birth trauma of newborns, treatment of birth injuries, rehabilitation, recovery from injuries
Comments ()
Characteristic
The psychological characteristics of a child with mental retardation are compiled according to those mental functions that are impaired in him.
Cognitive abilities
Thinking in children with mental retardation:
- normal level of development of visual and effective thinking;
- for the development of visual-figurative thinking, repeated repetition of the task is necessary;
- unformed skills to carry out analysis and synthesis operations;
- poorly formed verbal and logical thinking.
Correctional classes with children suffering from mental retardation should be aimed at developing thinking taking into account these features. They are able to classify objects according to one characteristic: color or shape, for example. The main thing is to eliminate distractions that significantly reduce performance, patiently repeat the task several times and rely primarily on visual-effective thinking, which is developed in them almost the same way as in their peers. In this regard, they have much better prospects for mastering the material when compared with those who have been diagnosed with mental retardation.
Memory in children with mental retardation:
- unstable;
- unproductive;
- involuntary prevails over voluntary;
- visual prevails over verbal;
- minimal self-control, lack of cognitive activity and motivation when learning and reproducing material;
- inability to use memorization techniques and organize memorization work;
- short-term memory is most affected;
- in the presence of interference, the memorization process practically stops;
- Material learned with great difficulty is quickly forgotten.
All of the above specific features of memory in children with mental retardation must be taken into account by teachers and psychologists when organizing classes and by parents when doing homework. The work should be structured in such a way that the support is involuntary and visual memory, and not voluntary and verbal.
Attention:
- scattered;
- weakened if information is presented verbally;
- unstable;
- reduction in parameters such as volume, selectivity, concentration and distribution.
Correction of attention is aimed at increasing volume and concentration. In classes, distribution and constant switching between different types of activities is necessary. Creative assignments are welcome.
Perception:
- superficial;
- slow process of formation of interanalyzer connections:
- deficits in auditory-visual-motor coordination;
- slow speed of building a single, integral image in a presentation.
Correction of perception is aimed at improving subject-research activities and mastering sensory standards. Games to improve coordination, spatial orientation and develop fine motor skills are welcome.
Speech:
- poor vocabulary;
- impaired sound pronunciation;
- unformed lexical and grammatical structure;
- problems with coherent speech;
- defects of the articulatory apparatus.
To develop speech, classes with a speech therapist are simply necessary. At home, parents need to read and talk more with their child. It is recommended to ensure that he constructs sentences correctly and that his speech is coherent.
Interpersonal communication
The process of interpersonal communication in children with mental retardation is difficult due to the inferiority of the prerequisites necessary for successful socialization:
- low cognitive motivation;
- insufficient speech activity;
- defective speech and mental activity;
- immaturity of many components of speech activity.
Therefore, interpersonal communication is characterized by the following features:
- episodic in nature (they are rarely included in games);
- working and playing alone;
- uncoordinated actions in pairs;
- role-playing game is not a joint activity, since there is practically no communication within it;
- inability to fully and clearly answer questions posed, formulate a question independently, speak out, listen to others, maintain a conversation;
- lack of attachment to anyone.
Children with mental retardation are much more willing to play with those who are younger in age. Often, against the background of failed interpersonal contacts, social phobia develops and serious problems with social adaptation arise.
Emotional-volitional sphere
In children with mental retardation, immaturity of the emotional-volitional sphere is observed. Its manifestations:
- emotional instability;
- lack of independence;
- lability;
- easy suggestibility;
- weakness of willpower;
- self-doubt, low self-esteem;
- causeless worry, increased level of anxiety;
- instant mood changes, contrasting emotions;
- inadequate cheerfulness, gaiety.
Children with mental retardation cannot correctly assess:
- situation: they react too aggressively to any failure and difficulties;
- emotional state of others: during the funeral they can laugh and have fun;
- own emotions.
This is interesting! Children with mental retardation, characterized by emotional immaturity, perfectly recognize emotions from facial expressions and pictures. Compared to their peers, they almost 100% find grimaces of anger, suffering and joy.
Clinical signs
It is important to understand that mental retardation is not a serious diagnosis. This type of disorder is at an intermediate level between the normal state of the child and pathology. Patients do not have significant problems with hearing, speech, motor activity and emotional state. The main difficulties are related to the child’s social adaptation and his learning abilities. In some cases, mental retardation may have its own characteristics of manifestation, but there is a characteristic set of clinical signs that should be the reason for a more detailed examination:
- Insufficiency of the emotional-volitional sphere is the first symptom. It is difficult for children to perform necessary tasks, including household tasks, if they do not bring positive emotions and do not arouse interest. This can cause problems with self-care.
- Poor attention is a typical manifestation of mental retardation. Children have difficulty concentrating even for a short period of time and are unable to perform several tasks at the same time. Often this symptom develops in combination with increased motor activity and emotional overexcitation. This complex is classified as a separate diagnosis “attention deficit hyperactivity disorder”.
- Impaired perception is another sign of mental retardation. The child can identify familiar objects, but it may be difficult for him to recognize them in an unknown environment. There may also be difficulties with orientation in space. Full work with the patient can partially improve the situation or even completely eliminate such disorders.
- Memory deficit has a characteristic feature - children perceive and remember verbal material worse. If they are given the opportunity to assimilate new information through visual images or text, the difference between the progress of children with mental retardation and those without this diagnosis will be absent or insignificant.
- Speech problems manifest themselves in different ways. A mild degree of mental retardation is characterized by a slight delay in speech while maintaining its quality. However, in severe forms there is a significant lag behind peers, a violation of the lexical and grammatical components.
- Thinking disorders apply to all forms of this process. Children have difficulty with logic, analysis, comparison and generalization of facts. This can be diagnosed when performing various logical tasks.
The Clinical Brain Institute offers individual diagnostic and adaptation programs for children with mental retardation. It is worth understanding that this diagnosis will not be an obstacle to visiting children's educational institutions, working in a team and other types of social activity. Full-fledged work can completely eliminate all differences between children without disabilities and patients with mental retardation, and their learning success will be almost the same.
Psychological characteristics
A child with mental retardation has features of mental development that differ from the symptoms of other similar pathologies. This is necessary to know to differentiate the diagnosis.
Differences from mental retardation:
- partial rather than complete impairment of cognitive activity;
- high potential for further development;
- It is not the mental functions themselves that suffer, but the prerequisites for intellectual activity (phonemic hearing, speech, attention);
- spasmodic dynamics of mental activity;
- ability to cooperate with adults;
- the presence of emotions in gaming activities;
- a vivid manifestation of emotion;
- often have a knack for drawing.
Differences from pedagogical neglect:
- lack of education and attention from adults is only one of the reasons, while in neglected children it is the only one;
- behavior is caused by deviations in the emotional-volitional sphere and cognitive abilities, and not by problems in moral and legal consciousness;
- are rarely distinguished by deviant behavior and rebellious character;
- know how to interact with adults.
The success of treatment and correction will depend on the correct diagnosis.
Diagnosis of mental retardation and methods of correction
To diagnose mental retardation in a child, it is necessary to consult several specialists who can confirm or refute this condition. This is a speech therapist, defectologist, psychologist, neurologist, pediatrician, and also a psychiatrist.
To diagnose CPR, the following is necessary:
- Detailed history taking.
- Carrying out CT, MRI, as well as an encephalogram, the results of which may indicate the presence of physiological reasons for the possible development of mental retardation.
- Conducting a psychological and pedagogical examination, during which the child’s ability to think and play activities is established. A diagnosis of memory, attention, as well as the emotional-volitional sphere of the child is carried out.
- Detailed examination of speech features.
If, as a result of studies, diagnostics, and consultations, this condition is confirmed, the baby needs corrective measures. Treatment is complex and requires the involvement of a whole group of different specialists. In the learning process, an emphasis on repetition, frequent changes of activities, and visualization of educational materials is important.
What is important to pay special attention to in the process of correctional work:
- An increase in the number of cognitive processes.
- The emotional sphere of the child, which is normalized as a result of active activities in a playful way.
- Normalization of speech activity, which is possible during regular speech therapy classes.
Classifications
Classification by Pevzner and Vlasova
M. S. Pevzner - defectologist, psychiatrist, psychologist, candidate of medical sciences and doctor of pedagogical sciences. Professor. T. A. Vlasova is a psychologist, defectologist, Doctor of Psychology, professor, academician. Years: 1972-1973.
- Uncomplicated psychophysical and mental infantilism
The emotional-volitional sphere corresponds to the development of younger children. Playful activity prevails over cognitive activity. This leads to inattention and learning problems.
- Secondary ZPR
The exhaustion of mental functions is caused by various biological factors that occurred during pregnancy or in the first year of the baby’s life.
Lebedinskaya classification
K. S. Lebedinskaya is a child psychiatrist and defectologist. Year: 1982. The basis is the classification of Pevzner and Vlasova, supplemented and expanded.
- Constitutional ZPR
Corresponds to uncomplicated mental and psychophysical infantilism according to the classification of Pevzner and Vlasova. Such children show bright, but superficial and unstable emotions. They are always in a high mood, they are mediocre and naive. They are distinguished by their gracefulness - an infantile body type. ZPR is caused by hereditary factors and complications during pregnancy.
- Somatogenic ZPR
Firstly, it occurs against the background of diseases suffered by the baby in the first year of life. Secondly, it is complicated by neurotic deviations. Such children are not self-confident, fearful, capricious, and feel their physical inferiority. All this ultimately leads to somatogenic infantilism - delayed emotional development.
- Psychogenic mental retardation
The main reason is unfavorable upbringing conditions, starting from a very early age and lasting for a long time.
- Cerebral-organic mental retardation
The most common type of ZPR. I. F. Markovskaya (Candidate of Psychological Sciences, Associate Professor) identifies another mini-classification within this group (1983).
1. Mental instability. Manifests itself in the form of hyperactivity, excessive noise, loudness, rudeness and conflict. But these children’s emotions are short-lived, so within a minute they will be playing with those with whom they just quarreled or even fought.
2. Mental retardation. Such children are dependent, indecisive, timid, slow, and too attached to their parents. They do not participate in joint outdoor games with others, they quickly get lost and cry when something is demanded of them.
Kovalev's classification
V.V. Kovalev - psychologist, psychotherapist. Year - 1979.
This is a classification of mental retardation caused by biological factors:
- dysontogenetic - mental infantilism;
- encephalopathic - organic lesions of the nervous system;
- secondary due to sensory defects - visual and hearing impairments;
- social deprivation - hospitalism.
Today, Lebedinskaya’s classification is most actively used in practice. Although she will soon be 40 years old. In connection with new standards of training and the changed realities of modern life, experts have long been talking about the need to create a more relevant typology of ZPR.
Diagnostics
The presence of mental retardation in a child can only be confirmed by special diagnostics. Specialists in the field can understand the nature and depth of existing violations during a comprehensive examination:
- psychotherapist;
- speech pathologist;
- psychologist;
- speech therapist;
- pediatrician.
All of them are included in a special medical and pedagogical commission, at which the diagnosis is confirmed or refuted, a final decision is made, and recommendations are given on the further development of the child. In addition to psychological characteristics, they carefully study dynamics (data are provided for the last 2-3 years):
- school performance;
- the nature of errors in mathematics and the Russian language;
- handwriting features;
- state of motor skills;
- pace of activity and many other aspects.
The commission is also provided with the results of a full medical examination and medical history.
Based on the data obtained, a conclusion is made whether the child has mental development delay. But, as mentioned earlier, a medical diagnosis of mental retardation has not been made since 1997. In conclusion, terminology from the following part of ICD-10 is used:
Diagnosis and treatment of mental retardation in children
Diagnosis of mental retardation is carried out with the participation of a child psychologist, neurologist, speech therapist and other specialists. It is important to conduct a brain examination to promptly identify possible disorders. Doctors at the Clinical Institute of the Brain recommend that parents provide all the necessary medical history data that may be important in making a diagnosis. Open and closed traumatic brain injuries, conflict situations in the family and team, stress and other factors that could affect the normal development of the child have enormous diagnostic value. In addition, you will need an encephalogram and other studies that will allow you to assess the degree of development and level of functioning of the child’s nervous system.
Treatment of mental retardation includes work with specialized specialists, including a speech therapist and a psychologist. It is important to follow their recommendations and continue exercising at home. Also important is the child’s social adaptation in children’s groups, which can only be ensured by attending general education and preschool institutions. If the diagnosis persists in the lower grades, it is recommended to attend a specialized school. The program in such institutions remains general, but the small number of children in classes and the presence of additional correctional classes make it possible to carry out full-fledged work with children.
The Clinical Institute of the Brain has all the necessary conditions for diagnosing and correcting mental retardation. However, doctors emphasize that full-fledged work with the patient also includes homework and ensuring a normal emotional climate in the family. When preparing to give birth and raise children, you have the opportunity to visit a psychologist and receive succinct recommendations on how to avoid problems and create the most comfortable conditions for the child’s development, not only physically, but also emotionally.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 4/5 — 1 votes
Share article on social networks
Education
Where and how can a child with mental retardation study:
- integrated education in secondary schools;
- correctional and developmental education based on a person-centered approach in general educational institutions;
- training in educational institutions of the VII type, where all the features of the educational activities of children with mental retardation are taken into account as much as possible.
In 2015, an important document was approved regulating the education of children with mental retardation in secondary schools. This is the “Adapted basic general education program for primary general education for students with mental retardation.” It is included in the “Special basic general education programs of primary general education of the Federal State Educational Standard”. This system is being implemented in regular educational institutions (not correctional) throughout the Russian Federation from September 1, 2021 in accordance with the Letter of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation dated June 7, 2013 “On correctional and inclusive education of children.”
From this moment on, children with mental retardation have every right to study not in a correctional school, but in a regular general education school, together with their normally developing peers. In this case, teachers and parents should take into account the following teaching features:
- they require more attention and individual approach;
- they study according to a separate, simplified program;
- Problems in mastering the material are not due to laziness and negligence, but to inability.
Educational psychologists insist that it is much more productive to send a child with mental retardation to a specialized correctional school or transfer him to home schooling.
Ways to prevent the disorder
By influencing the causes of speech delay, it is possible to effectively carry out prevention, treatment and reduce morbidity.
The main preventive measures include:
- adherence to sleep and wakefulness;
- joint holding of family holidays and events where children are given due attention;
- early start of classes with a speech therapist individually or in special correctional groups;
- reading children's literature, studying children's poems together, walks, trips;
- a balanced diet that excludes or reduces bread, cookies, eggs, milk, honey, candy, potatoes, beets, crackers, chicken, shrimp, chocolate, exotic fruits and berries from the baby’s diet;
- psychotherapy in a group.
An indicator of the effectiveness of treatment is the compliance of speech and mental development with the age norm.
Advice for patient and attentive parents on what to do for children with mental retardation:
- Carry out regular medical examinations with the involvement of a neurologist, pediatrician, speech therapist, otolaryngologist, orthopedist, and ophthalmologist.
- Develop the child’s understanding of speech using simple instructions such as “give me a book”, “take a cup from the table and take water to grandma.”
- You need to read, sing, talk with your baby, voicing all your actions and surrounding events and try to provoke him into dialogue.
- Without waiting for the child to speak, it is necessary to develop the baby’s sensory skills, teach him to distinguish objects by size, shape, color, and develop fine motor skills of the hand.
The video below shows how to teach your child shapes and colors:
Treatment and correction
Depending on the type of mental retardation and the individual characteristics of the child, specialized specialists develop a correctional and developmental program for the child to study. It includes various blocks that provide an integrated approach to solving existing problems.
Microcurrent reflexology
This is a hardware effect of electrical impulses on bioactive points of the brain, the so-called neuroreflex zones. Targetedly restores the functioning of the nervous system exactly where there are disturbances. Microcurrents selectively process the brain centers responsible for intellectual abilities, speech activity, diction, and vocabulary.
Organized in a hospital setting. True, not all parents give consent to the procedure.
Psychological and pedagogical correctional classes
A child with mental retardation should regularly attend psychologist classes. The goal is to adjust mental development in such a way that it improves his quality of life. Among the main tasks:
- increase the level of intellectual, emotional and social development;
- develop gross and fine motor skills;
- expand your vocabulary and conceptual apparatus.
Parents have the right to know what the program of the psychologist who works with their child includes. Points that raise doubts or mistrust must be agreed upon in advance.
Psychological work with children suffering from mental retardation involves the use of a variety of techniques.
Psychotherapeutic areas:
- isotherapy;
- sand therapy;
- music therapy;
- puppet therapy;
- fairytale therapy;
- logorhythmics;
- methods of object-sensory therapy.
During classes, the psychologist organizes didactic games with multi-colored stripes, cubes, sticks, geometric shapes (including three-dimensional ones) and special cards. Examples of several such games are presented below.
"Guess the Emotion"
It is carried out either in a group of 5-6 similar children with mental retardation, or in pairs with a psychologist. Cards with schematic representations of various emotions are placed on the table. It is proposed to take one of them at random, name what is in the picture, and try to depict this feeling using facial expressions, voice, and gestures. You can make the task more difficult and ask them to name the situation in which this emotion most often manifests itself.
"Find the number"
Pictures and three-dimensional figures of different numbers are laid out on the table. They all differ in size and color. The psychologist names a number - you need to select all the matches from the proposed material (for example, all twos or eights).
"Mood Lotto"
There are cards on the table with animals with different faces on them. The psychologist names an emotion (shows a picture of it or depicts it himself) - the child must choose the right card for it.
"Magic bag"
Small voluminous things that are easily recognizable by touch are put into a beautiful bag: a mirror, an alarm clock, a pencil, a notepad, a ruler, etc. You need to put your hand in there with your eyes closed, take out any object and guess what it is.
"Mood Palette"
There are cards with different shades of mood on the table. The psychologist asks the question: “How do you feel now?” — the child must answer using a drawing. After this, the question is transformed several times: “How is your mother feeling today?”, “What do you think is your cat’s mood?” etc.
Alternative techniques
Additionally, specialized specialists can prescribe modern, non-traditional correction methods:
- hippotherapy;
- canistherapy;
- dolphin therapy;
- feline therapy.
Timely and competently carried out psychocorrectional work gives positive results.
Delayed psycho-speech development in a child: causes, prognosis and treatment methods
Delayed psycho-speech development is a consequence of deviations in the formation of the brain and central nervous system. There are many reasons for this disorder, and even more methods of treatment. Neurologists say: this condition can be corrected, the most important thing is to begin correction as early as possible.
Ekaterina Cherkaeva , how to determine ZPRD in a child, what to do if you suspect a disease and what are the prognoses of this condition. “Kemerovo Woman of the Year” for the introduction of a new method of neurorehabilitation in the Kemerovo region.
“Peculiarities in a child’s behavior can be noted as early as one and a half years old”
– Delayed psychospeech development (DSRD) should be officially determined by members of the psychological, medical and pedagogical commission. Usually a neurologist, speech therapist, psychiatrist, and psychologist are present there. It is difficult to officially make such a diagnosis before 3-5 years. But correction can and should begin as early as possible. In my experience, already at one and a half years old one can notice peculiarities in the child’s behavior, in his reactions to the environment, play detail, and the subtleties of his perception of the world. Of course, you need to pay attention to such a child and take action.
A neurologist can determine the risk of mental development delay in a child. And the next specialists who will observe the little patient will pay closer attention to the features in the baby’s development.
To answer the question whether the disease is congenital or may appear later, you need to understand the reasons for mental retardation.
There are many reasons: these can be somatic diseases, for example, hypothyroidism, renal failure, frequent pneumonia. Such children spend a long time and often undergo treatment in hospitals. These diseases delay the maturation and development of the central nervous system, which can lead to speech delays and many other problems.
Also, the reasons may be of psychogenic origin, this may be due to unfavorable living conditions: lack of communication with adults and peers, neglect. Sometimes PVRD is caused by mild brain damage or genetic factors. For example, parents say that the child’s father also spoke only at the age of five, and this did not affect him in the future. As for changes in the brain: these could be calcifications, expansion of the lateral ventricles.
Another cause of PVD is hearing or vision impairment from birth. If there are such problems, parents should worry about the consequences in advance and begin correction.
Parents rarely complain about their child’s mental retardation. Mostly they come with complaints of speech delay. But we must understand that these things are interconnected.
“It is difficult to distinguish delayed psycho-speech development from mental retardation”
– These children have problems with attention and concentration. It is difficult to teach them something new. Gaming activity is quite intermittent and inconsistent. They “jump” from one thing to another, don’t know what to take on, and absolutely cannot do one thing for a long time. Any extraneous stimuli instantly distracts the child and switches his attention. Such a child quickly gets tired during strenuous activity, immediately becomes hyperactive, or his attention evaporates.
Memory in children with mental retardation disorders may be selective. Parents often say that their child remembers some things well, but cannot retain others at all.
Such children perceive visual information better than auditory information. It is difficult for them to carry out any command or complex instruction the first time. He can remember the first part of the instructions, but not the second. Children with delayed psycho-speech development perceive visual aids better.
They have problems with the emotional-volitional sphere, they cannot force themselves to do something, they react negatively to refusals, and they like to manipulate their parents. They don’t want to do some task, and they resort to tears and hysterics. This is a fairly common occurrence with mental retardation.
Manifestations depend on the age of the child. From 2 to 3 years old, your indicators, from 3 to 5 – your own. A neurologist or defectologist must monitor the condition of a particular child and evaluate it from his professional point of view. These guys have problems with motor skills; many do not know how to ride a bicycle, for example, because they cannot coordinate their body. One of the manifestations of motor clumsiness: the inability to jump on two legs. Also, children with mental retardation disorders are characterized by a certain infantilism.
It is quite difficult to distinguish between mental retardation and mental retardation, especially at a young age. Until the age of five, differences are almost impossible to detect, so everyone is usually diagnosed with mental retardation. In children with mental retardation, almost all areas are impaired at the same time. They are difficult to corrective work, it is more difficult for them to assimilate information. A child with DLD may have poor speech and poor concentration, but may have good thought processes.
“Impairments with ZPRR are reversible”
– All violations of the emotional-volitional sphere: problems with memory, concentration, perception, attention, thinking, self-regulation, instability of emotions - these are all reversible changes that need to be corrected before school.
If you see that a child is having difficulty learning, don’t wait for a miracle, but act. Many parents think that everything will “go away on its own” and the child will learn everything gradually. But it is important to notice the problem in time and begin to correct it. It’s better to play it safe and take your baby to a neuropsychologist for diagnostics. It's available now. The specialist will check how the child performs exercises on thinking and attention. And then it will be possible to draw some conclusions regarding the child’s condition.
Standardly, when dealing with mental retardation, people work with a speech pathologist, a psychologist, or a speech therapist, since speech problems will not go away. Periodic monitoring by a neurologist is required. But a neurologist is not the main specialist for this disease. The correction here, in my opinion, should be based on a pedagogical program, according to which you need to study from 3 to 5 times a week, depending on the violations. I recommend going to a neurologist once every three months for intensive courses of rehabilitation treatment, which may include drug treatment, massages, micropolarization, magnetic therapy, and Tomatis therapy. The approach to treatment depends on the neurologist.
“It’s too late to start correction at school age”
– The outcome of mental retardation is possible to be positive, without consequences for the child, if everything is done competently, intensively and, most importantly, before school. Ideally, everything should be restored within 4-5 years. Of course, a lot depends on the cause of ZPRR. For example, with organic brain damage, everything is not so simple. If problems with overprotection, and the parents themselves make the child weak-willed and self-centered, then you need to work more with a psychologist, including a family psychologist.
The outcome of mental retardation is influenced by many factors: from the responsibility of the parents and the severity of the disorders to the age of the child. When a child is first brought to a neurologist at the age of 8, and he clearly has serious problems, he cannot cope with the school curriculum, this is bad. At this age it is too late to start correction. That is, of course, it can and should be started, but the prognosis for such a child will not be very good, and the consequences for his future life will remain quite serious.
I can understand some parents who wait until the child grows up and some symptoms disappear on their own. This happens, it seems that the child grows, matures, his attention and concentration become better. But with ZPRR this is not fully restored, and it will be difficult for the child at school, and time will be lost. Now all the information is on the Internet, parents can read and study everything. If you have any doubts, contact a neurologist, speech pathologist, or several specialists at once.
“With proper treatment, the child does not have any consequences that will interfere in later life”
– Standard methods for correcting delayed psycho-speech development are drug treatment, electrophoresis on the neck, massage of the cervical-collar area. Speech therapists can begin correction in their field from the age of five.
Each neurologist has his own treatment regimen for the same child. There are parents who go to several neurologists at once. It all depends on the experience of the specialist, his perception of the child, and knowledge.
Personally, I believe that today using only drug treatment is ineffective. Mental and speech delays have become very common among children, and everyone is prescribed the same nootropics, which can be taken endlessly. The basis should be pedagogical influence. You can't go far on medication alone.
The purpose of modern methods depends on the symptoms of the disease in the child. For those who have serious problems with auditory concentration, Tomatis therapy is suitable, which is aimed at training precisely this skill.
Brain magnetic therapy is usually used to sedate a child to make him calmer, more alert and more focused. Not suitable for every small patient. And classes with a speech pathologist, speech therapist and psychologist are suitable for absolutely everyone.
If corrective work with a child is organized correctly, there will be strong positive dynamics. As the child grows up, after diagnosis, we no longer find changes in him that will interfere in later life.
What should parents do?
Psychologists and teachers who work directly with children who have mental retardation give useful recommendations to parents to speed up their development.
To begin with, parents will have to not only understand, but also accept the fact that the child will learn more slowly than his peers and lag behind them in his studies. In order not to demand too much from him, to be patient with his characteristics, they need to be studied and taken into account when communicating and studying.
Homework alone cannot solve the problem of mental retardation. Therefore, the second step for parents who want to help their child is to seek qualified help from specialized specialists - a special education teacher, a psychologist or a psychotherapist. Taking into account individual characteristics, they will give recommendations on what exactly needs to be done.
General tips:
- Exercise daily for 30-40 minutes.
- Pay more attention to the child, organize time together, communicate, involve other relatives.
- Provide a comfortable atmosphere in the family.
- Normalize the daily routine, introduce a healthy lifestyle, provide a balanced diet, increase physical activity and stay in the fresh air.
- Communicate with other parents of the same children (for example, through communities on social networks).
- Organize communication with peers.
- Don't tell your child that he is special. Do not regret that he is not like everyone else.
- Assign household chores, animal care, teach self-care.
- Don't raise your voice, be patient no matter what happens.
- Keep a diary to note all your successes - these entries will help you adjust your future work.