Every mother watches her children with interest and looks forward to their first words. But sometimes they do not appear for a long time, or speech is filled with individual sounds. Some parents notice that children pronounce words incorrectly or distort them, but do not know when their child needs a speech therapist and for what problems.
Often, mothers and fathers turn to a specialist only when the child is left for the second year at school or is forced to leave the kindergarten/school due to a developmental delay, the basis of which is speech. We'll tell you when to contact a speech therapist with your child to avoid problems in the future.
Signs of normal speech development
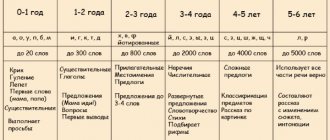
The first reaction of a newborn baby is to cry. Afterwards it transforms into humming - the production of individual sounds. By six months, the baby is already babbling with might and main, that is, pronouncing similar syllables. He can already use them to express his demands and desires.
- The first stage of active speech begins at one year of age. By this time, the baby begins to pronounce individual words and connect them into simple sentences. The vocabulary increases; by the age of one and a half years, children begin to form phrases of four words.
- At 2-3 years old, the baby is already actively communicating with peers. His speech is far from ideal, he swallows parts of words and does not pronounce half of the sounds, but is able to remember simple poetry.
- At three years old, whistling sounds [С], [С'], [З], [З'], [Ц] appear, but they are not always pronounced clearly - this is normal.
- At the age of four, the hissing sounds [ZH], [SH], [CH'], [SH'] appear; children easily formulate their thoughts and conduct full-fledged dialogues with adults, which are limited only by their level of knowledge about the world around them.
- At five or six years old, the most complex sounds appear - sonorous sounds. These include [P], [P'], [L], [L']. Children are mastering speech better and better, and they almost no longer make mistakes. Their vocabulary contains about 2 thousand words.
- By the age of seven, the child pronounces all the sounds of the Russian language and pronounces them correctly. Actively retells stories using pictures, easily changes intonation and uses about 3,500 words in communication.
If your baby develops according to the scenario described above, then the child needs a speech therapist at 2.5 years old. The specialist will diagnose speech development, make sure that the baby is developing normally, and tell you the nuances of the current state of speech, what you should pay attention to.
Advice from a speech therapist for parents of 4-year-old children:
All speech therapists advise working with children not only in a group, but also at home, that is, constantly strengthening and improving the result. There are a lot of games and exercises for this, since the best communication with a child and his learning at an early age occurs in a playful way.
It is imperative to pay attention to the child’s fine motor skills, because, as you know, our speech is at our fingertips. To do this, play finger games (about 5 minutes every day):
Articulation gymnastics is no less important . It is necessary to develop and warm up the tongue and lips so that the child speaks as clearly and clearly as possible. To do articulation exercises, you need to sit with your child in front of a mirror (so you can see each other in it). Next, you can perform exercises of this type:
The following exercises develop hearing and onomatopoeia .
Recommended age to visit a specialist
A speech therapist is a specialist who eliminates speech defects. People turn to him for various reasons. Sometimes this is not pronouncing a sound, in other cases it is a long silence of the baby. The age at which a child needs a speech therapist depends on the specific problem.
The main cause for concern is the lack of speech. Normally, children begin to speak at one year of age. Don't worry if the words appear a little later. Experts consider the critical age to be two and a half years. If by the age of 2.5 years the baby has not spoken or has only a few words in his speech, then there is a delay in speech development. A comprehensive examination by specialists is recommended here.
If you have questions about the speech of a child under 2 years old, or you doubt his correct development, then it makes sense to go to a pediatrician. The speech therapist accepts children from the age of 2 years.
Many people do not think about at what age they should contact a speech therapist with their child, believing that speech will develop on its own. That in kindergarten or school teachers will correct all problems. Then the child is asked to leave a private kindergarten due to problems with speech development or is left for the second year at school. There is a practice of such cases and they are not isolated.
The speech therapist conducts a speech therapy examination, which resembles a comprehensive testing of the child’s abilities. He checks whether the child understands speech, whether the child follows simple instructions, how many words are in his speech, whether he knows how to change words by numbers, etc. A speech therapist is a correctional teacher. He conducts special classes that are aimed at evoking and developing the baby’s speech. This slow process sometimes takes several years.
The parent has many reasons for concern, including the absence of humming or babbling, the baby’s lack of understanding of spoken speech, and delayed physical development. This may be a symptom of serious problems. Therefore, consultation with various specialists, not just a speech therapist, will be required. Before taking the child to a speech therapist, parents can show him to a psychiatrist, audiologist (to rule out hearing impairment), or a neurologist.
Preventative examination by a speech therapist - is it necessary or not?
Home - About speech therapy - Preventive examination by a speech therapist - is it necessary or not?
As a rule, parents do not attach much importance to preventive examinations by a speech therapist. And completely in vain, because... Today, many children have some form of speech impairment.
Preventive examinations are a common occurrence in medicine, take, for example, the examination of a child in the first year of life, when after a certain period of time the baby is examined by various specialists (neurologist, ophthalmologist, surgeon, etc.). And no one doubts the need for such examinations, since they are aimed at tracking the dynamics of development. In addition, with their help, it is possible to timely identify any developmental disorders, since there is no guarantee that the baby’s health status will not change due to various factors. And if any problems arise, early diagnosis will help resolve them most effectively.
But, if no one doubts the need to monitor the child’s health, then little attention is paid to the preventive examination of a speech therapist in our society. The opinion has become firmly established that a speech therapist only works with children 4-5 years old, and if there are any problems, then you can wait and they will resolve themselves by this age. This is supported by numerous examples from the personal experience of friends and relatives (“Mine only started talking at five and nothing, now he’s chatting incessantly,” “And you started talking too late, you’ve grown up, you talk”). And therefore, parents’ vigilance decreases, and they believe that it is not at all necessary to contact a speech therapist. Yes, there are cases when a child begins to speak later than his peers, and then speech appears and in a few months the baby catches up. Alas, the opposite situation often occurs when a child does not begin to speak by the age of three, five, or six, and the lag in speech leads to a secondary lag in mental development. This explains the importance of timely diagnosis of speech by a speech therapist.
Having opened the children's medical record, we will see that it is recommended to visit a speech therapist 2 times: at 3 years old (before entering kindergarten) and at 6 years old (before school).
But there are methods for examining speech at an earlier age. And if parents or doctors see a delay in a child, then a speech therapist can conduct a speech examination up to 3 years.
It would seem, how can one check speech if it, as such, does not yet exist? Let's figure it out. The baby cannot speak, but, nevertheless, he communicates with his mother and the adults around him with the help of a smile, facial expressions, a cry, a gesture, i.e. uses nonverbal communication. The baby looks at the faces of those around him and copies their facial expressions. There are a lot of funny videos on the Internet where babies of 3-4 months repeat their sounds or intonation after mom or dad. With normal development, a child should have about 10 words by the age of one year (Example: “day”, “mom”, “dad”, “ki-kisa”, “lala”, etc. These will most likely be onomatopoeias or fragments of words. At the same time, the baby can show a lot, even if he cannot pronounce it on his own (i.e., these words are in the passive dictionary, the child understands them.) Everyone is familiar with the situation when a one-year-old baby’s mother asks: “Where are your ears? Eyes? Back?", and the child points with his finger. "Show me which car passed?" - the child imitates a truck and “snorts,” while he says “beep beep” to a passenger car.
If the baby is “silent, like a guerrilla,” and makes no attempts to communicate, this is an alarming factor.
Let's take a closer look at what a speech therapist will study in a child under 3 years old.
First of all, the specialist will find out from the parents information about the course of pregnancy and childbirth. Then he will ask how motor development proceeded (when he began to hold his head up, roll over, sit, etc.), how the stages of humming and babbling went through (age, activity of these processes). He will ask how feeding was organized (breastfeeding or artificial feeding), whether there were any problems during feeding (refused to latch on, whether he burped often). All this will give an idea about the child’s health, the level of his physical development, and possibly about some deviations, the presence of which must be taken into account.
When diagnosing a child, attention is paid not only to the words the child uses, but also to how the child understands speech. For example, by the age of one year, a baby can already show familiar toys, body parts, follow simple instructions (“Give me a pen,” “Bring a doll”) and understand the meaning of the word “no.”
At an older age (3 years), active speech is assessed more closely: whether it constructs simple sentences, whether it uses prepositions in speech (on, under, in). Attention is also paid to the development of phonemic hearing; at 3 years old, the child can already distinguish similar words by ear (house-lump, mouth-mole, rat-lid). When assessing sound pronunciation, pay attention to the sounds of early ontogenesis (P, B, T, D, M, N, V, F, X, K and their soft pairs and vowels).
At older ages (5-7 years), more stringent requirements are imposed on the quantity and quality of children’s speech. First of all, sound pronunciation is studied (since by the age of 5.5 all sounds are normally pronounced). Phonemic hearing is also examined, but in addition to the ability to distinguish similar words, the ability to isolate a given sound from a word and the ability to determine where this sound is located (beginning, middle, end of the word) are tested. Vocabulary is not left without attention. Children are tested for knowledge of low-frequency words (Example: name “flower bed, monument, wreath, waterfall”), the ability to form new words (word formation) and change words by cases and numbers (word inflection). Much attention is paid to coherent speech (story based on a picture, life story, etc.).
All this is necessary in order to assess how prepared a preschooler is for school, since insufficient vocabulary, incorrect use of grammatical norms of the language and impaired phonemic hearing will interfere with the development of the school curriculum, so it is necessary to identify this and correct it before entering school.
How can parents understand whether a consultation with a speech therapist is necessary or not?
To do this, you need to pay attention to factors such as:
- does the child understand the speech of others;
- whether the first words appear by the age of one year;
- whether the words change over time or remain at the level of onomatopoeia (bi-bi-atina-masina-machine, meow-kitya-cat);
- does he use simple phrases (mom, let’s go for a walk);
- does it replace speech with gestures (points with a finger if something is needed without words);
- absence of phrasal speech by 3 years;
- incorrect pronunciation of sounds of early ontogenesis (P, B, M, N, X, G, T, D and their soft pairs, and vowels).
If you observe any of the above, then you should not wait 3,4,5 years; you should immediately seek help from a qualified specialist.
Examples from speech therapy practice
:
Nastya is 3 years old. They turned to a speech therapist because the girl did not even speak words, she communicated with gestures and individual sounds. According to the mother's stories, early development was delayed, the girl did not babble, and she started walking late. Fine motor skills are not developed, hands are weak. At the same time, speech understanding is intact. The girl was referred for consultation to a neurologist, ENT specialist, and audiologist. As a result of complex treatment over the course of six months, the girl began to pronounce individual words, and her motor skills improved.
Another example is Olya, 6 years old. Speech consists of individual syllables, spoken speech is not always understood, fine motor skills are not developed, and the passive vocabulary is below the age norm. When asked if they had consulted specialists before, my mother replied that the neurologist said to wait 5 years, as if she would speak on her own. Therefore, no measures were taken to correct the girl’s speech.
Denis, 5 years old. The child speaks a lot and well, but the sounds Ш, Ж, Р and Рь never appeared in his speech. During the consultation, the speech therapist examined all aspects of speech and identified the cause of the difficulties in sound pronunciation (the child had a “sluggish tongue”; he would not have been able to master these complex sounds on his own). The boy began to study regularly, and soon the problems with sound pronunciation were resolved.
As we see, in the second case, a lot of time will pass before the girl masters speech skills, and she will not be able to study in a public school. All this could have been avoided if the parents had consulted a speech therapist earlier.
Thus, a preventive examination by a speech therapist is necessary because it allows one to identify problems at an early stage, when the brain is even more plastic and will be better amenable to corrective influences. No matter what anyone says, if a child does not speak by the age of 3, it is better to immediately contact a qualified specialist rather than hope for a miracle.
Share:
Find out more about the Center's services and sign up for a consultation or lesson
You can call (812)
640-90-77
, or by filling out the form below.